The Center for Internet Security (CIS) released Version 8 of its CIS Controls document in May 2021. This document, consisting of 18 information security controls, is essential for organizations and security professionals to protect their data, networks, and systems.
A couple of clients I work with at the moment lack mature information security programs and struggle to navigate the overwhelming resources available. To address this, I recommend starting with concise and comprehensive CIS Controls. It provides an executive-friendly overview and specific control details for IT and security teams to implement effectively.
In this article let’s focus on Control 01 – Inventory and Control of Enterprise Assets. This control emphasizes actively managing and tracking all enterprise assets, including end-user devices, network devices, IoT devices, and servers. By accurately knowing and monitoring these assets, organizations can identify unauthorized or unmanaged ones and take appropriate action.
Maintaining an inventory of enterprise assets is crucial because organizations can only defend what they know. However, during my client engagements, I often discover inaccurate or incomplete inventories. This leaves their systems and organization vulnerable to potential attacks.
Recently, I conducted a gap assessment for a client lacking a mature security program. Despite prioritizing advanced security tools, they neglected to maintain a definitive system inventory. As a result, outdated and unpatched servers were discovered, posing significant risks. This lack of control coordination and oversight can have serious consequences.
To address this, organizations must implement policies and procedures to maintain an accurate inventory of all assets, including on-premises, cloud-based, and remote systems. Regular reviews and updates should be conducted, utilizing automated tools alongside manual verification. Comparing inventories with network vulnerability scans helps identify potential gaps and assign ownership for continuous updates.
With an accurate inventory, organizations can effectively protect their systems. This includes ensuring the latest security patches, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems are in place. Periodic checks of security tools on all systems are necessary for ongoing security assurance. By taking these steps, organizations can enhance their security posture and safeguard company and customer data.
For further information, feel free to connect with me on Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/jakeadebayo/ or via https://estreetsecurity.com to book an information security specialist today.
Objective: To establish and maintain a detailed enterprise asset inventory in an on-premises organization, you can consider using a combination of the following tools:
Project CISv8 Control 1.
-
Network Discovery and Inventory Tools:
- Nmap: Nmap is a powerful network scanning tool that can discover and map networked devices, identify open ports, and gather information about the systems on the network.
- Open-AudIT: Open-AudIT is an open-source network auditing and inventory tool. It scans the network to discover devices, collects hardware and software information, and maintains an up-to-date inventory database.
-
Configuration Management Tools:
- Ansible: Ansible is an open-source configuration management tool that can help with inventory management. It automates the process of collecting configuration data from systems, tracks changes, and maintains an inventory of configuration details.
- Puppet: Puppet is another popular configuration management tool that can assist in maintaining an inventory of on-premises systems. It can gather information about devices, manage configurations, and provide insights into the state of the infrastructure.
-
Asset Management Systems:
- Snipe-IT: Snipe-IT is an open-source asset management system that allows you to track and manage physical assets within your organization. It provides features like asset tracking, warranty management, and customizable inventory fields.
- GLPI: GLPI is an open-source IT service management and asset tracking system. It helps organizations manage inventory, track hardware and software assets, and maintain a centralized repository of asset-related information.
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools:
- Elastic Stack (formerly ELK Stack): The Elastic Stack, comprising Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana, can be utilized to collect, analyze, and visualize log data from various systems and devices. It can aid in identifying and monitoring assets within the organization.
These tools, used in conjunction, can help establish and maintain a detailed enterprise asset inventory in an on-premises organization. They assist in discovering devices, collecting configuration information, tracking changes, and providing visibility into the hardware and software assets across the infrastructure.
Project Objective
The project objective is to implement the CIS control 1 (Control 01: Inventory and Control of Enterprise Assets) in order to improve the organization’s asset management capabilities. This will be accomplished by ensuring that your organization:
- Has Established and maintains a detailed enterprise asset inventory.
- Has Implemented and complies with policies that address unauthorized assets.
- Utilizes an active discovery tool.
- Uses Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) logging to update enterprise asset inventory.
- Uses a passive asset discovery tool.
By implementing these safeguards, the organization will be able to improve its asset management capabilities and reduce its risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Scope of Work
Timeline
The project will be completed in two weeks. The following is a detailed timeline of the project:
Week 1
- Day 1: Kickoff meetings with stakeholders
- Day 2: Review existing asset inventory (if any)
- Day 3: Install and configure GLPI
- Day 4: Collect asset information using active and passive discovery tools
- Day 5: Import asset information into GLPI
- Day 6: Review and update asset inventory
Week 2
- Day 7: Address unauthorized assets
- Day 8: Configure DHCP logging
- Day 9: Test asset inventory
- Day 10: Finalize asset inventory
- Day 11: Train stakeholders on asset inventory
- Day 12: Prepare final report
- Day 13: Present final report to stakeholders
CIS Control 1 Safeguards Coverage
Safeguard 1: Establish and Maintain Detailed Enterprise Asset Inventory
- Week 1, Day 3: Install and configure GLPI (Done)
- Week 1, Day 4: Collect asset information using active and passive discovery tools.
- Week 1, Day 5: Import asset information into GLPI.
- Week 1, Day 6: Review and update asset inventory.
Safeguard 2: Address Unauthorized Assets
- Week 2, Day 7: Identify unauthorized assets.
- Week 2, Day 8: Remove unauthorized assets from the network.
Safeguard 3: Utilize an Active Discovery Tool
- Week 1, Day 4: Use active discovery tools to collect asset information.
Safeguard 4: Use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Logging to Update Enterprise Asset Inventory
- Week 2, Day 8: Configure DHCP logging.
- Week 2, Day 9: Use DHCP logs to update asset inventory.
Safeguard 5: Use a Passive Asset Discovery Tool
- Week 1, Day 4: Use passive asset discovery tools to collect asset information.
Resources
The following resources will be needed to complete the project:
Safeguard 1: Establish and Maintain Detailed Enterprise Asset Inventory
- Asset inventory software – GLPI is an open-source IT asset management software that can be used to implement the CIS control 1 (Control 01: Inventory and Control of Enterprise Assets). GLPI can be used to collect information about all of an organization’s assets, including their hardware, software, and network devices. GLPI can also be used to track the ownership of assets, their licenses, and their configurations. GLPI is a powerful tool that can help organizations to improve their asset management and security.
Here are some of the features of GLPI that make it the most appropriate Asset Inventory software for your organization:
- Asset Ownership: GLPI can be used to track the ownership of assets. This information can be used to ensure that assets are properly managed and that they are not being used by unauthorized users.
- Asset Licenses: GLPI can be used to track the licenses for all of an organization’s software. This information can be used to ensure that software is properly licensed and that organizations are not in violation of any licensing agreements.
- Asset Configuration: GLPI can be used to track the configuration of all of an organization’s assets. This information can be used to ensure that assets are properly configured and that they are not vulnerable to security threats.
- Alternatives (Commercial Tools)
- Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (compatible with GLPI)
- IBM Tivoli Asset Management (compatible with GLPI)
- Oracle Enterprise Asset Management (compatible with GLPI)
- SAP Asset Intelligence (compatible with GLPI)
- ServiceNow IT Asset Management (compatible with GLPI)
- Alternatives (Open Source Tools)
- Nagios (compatible with GLPI)
- Zenoss (compatible with GLPI)
- OpenNMS (compatible with GLPI)
- Cacti (compatible with GLPI)
- Munin (compatible with GLPI)
- GLPI (open source, compatible with itself)
Safeguard 2: Address Unauthorized Assets
- Commercial Tools
- Symantec Network Access Control (compatible with GLPI)
- Cisco Identity Services Engine (compatible with GLPI)
- Juniper Networks Secure Access Control (compatible with GLPI)
- Palo Alto Networks WildFire (compatible with GLPI)
- Check Point SandBlast (compatible with GLPI)
- Open Source Tools
- Snort (compatible with GLPI)
- Suricata (compatible with GLPI)
- IDSWall (compatible with GLPI)
- Bro (compatible with GLPI)
- nProbe (compatible with GLPI)
Safeguard 3: Utilize an Active Discovery Tool
- Commercial Tools
- Nessus (compatible with GLPI)
- QualysGuard (compatible with GLPI)
- Rapid7 InsightVM (compatible with GLPI)
- Tenable Nessus (compatible with GLPI)
- Open Source Tools
- OpenVAS (compatible with GLPI)
- Nmap (compatible with GLPI) – compatible with GLPI
- Zenmap (compatible with GLPI)
- Masscan (compatible with GLPI)
- ZMap (compatible with GLPI)
Safeguard 4: Use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Logging to Update Enterprise Asset Inventory
- Commercial Tools
- Microsoft DHCP Server (compatible with GLPI)
- ISC dhcpd (compatible with GLPI)
- Dnsmasq (compatible with GLPI)
- DHCPd3 (compatible with GLPI)
- DHCP Server (compatible with GLPI)
- Open Source Tools
- isc-dhcp-server (compatible with GLPI)
- Dnsmasq (compatible with GLPI)
- DHCPd3 (compatible with GLPI)
- DHCP Server (compatible with GLPI)
Safeguard 5: Use a Passive Asset Discovery Tool
- Commercial Tools
- Lansweeper (compatible with GLPI)
- ManageEngine OpManager (compatible with GLPI)
- SolarWinds Network Inventory Advisor (compatible with GLPI)
- Auvik Network Discovery (compatible with GLPI)
- InterMapper (compatible with GLPI)
- Open Source Tools
- Sniffers (compatible with GLPI)
- Packet captures (compatible with GLPI)
- Netflow (compatible with GLPI)
- IPFIX (compatible with GLPI)
- SPAN (compatible with GLPI)
Risks
The following risks have been identified for this project:
- The project may not be completed on time or within budget.
- The asset inventory may not be accurate or complete.
- Unauthorized assets may not be identified or addressed.
- The active discovery tool may not be effective in identifying all assets.
- The DHCP logging software may not be effective in updating the asset inventory.
- The passive asset discovery tool may not be effective in identifying all assets.
Mitigation Strategies
The following mitigation strategies have been developed to address the risks identified for this project:
- The project will be closely managed to ensure that it is completed on time and with no extra budget than we already incur.
- The asset inventory will be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure that it is accurate and complete.
- A process will be developed to address unauthorized assets.
- The active discovery tool will be tested to ensure that it is effective in identifying all assets.
- The DHCP logging software will be configured to update the asset inventory on a regular basis.
- The passive asset discovery tool will be tested to ensure that it is effective in identifying all assets.
Compliance Documentation
For an IG3 implementation of CIS Control 1, the following policy documents are required:
- Asset Inventory Policy: This policy defines the requirements for inventorying all assets within the organization, including hardware, software, and data.
- Asset Classification Policy: This policy defines the criteria for classifying assets based on their value and sensitivity.
- Vulnerability Management Policy: This policy defines the requirements for identifying, assessing, and remediating vulnerabilities in assets.
- Incident Response Policy: This policy defines the procedures for responding to security incidents, including detecting, investigating, and containing incidents.
These policy documents should be developed in accordance with the organization’s overall security policy framework. They should be reviewed and updated on a regular basis to ensure that they reflect the current state of the organization’s assets and security risks.
In addition to these policy documents, an IG3 implementation of CIS Control 1 may also require the following technical controls:
- Asset discovery and inventory tools
- Asset classification tools
- Vulnerability management tools
- Incident response tools
These technical controls can help to automate and streamline the implementation of the policy requirements. They can also help to improve the accuracy and completeness of the asset inventory, vulnerability assessment, and incident response processes.
Here are some additional details about each of the policy documents:
- Asset Inventory Policy: This policy should define the following:
- The types of assets that should be inventoried
- The frequency of asset inventories
- The methods for asset inventory
- The format of asset inventory reports
- Asset Classification Policy: This policy should define the following:
- The criteria for classifying assets
- The impact of asset classification on asset management
- Vulnerability Management Policy: This policy should define the following:
- The processes for identifying vulnerabilities
- The processes for assessing vulnerabilities
- The processes for remediating vulnerabilities
- Incident Response Policy: This policy should define the following:
- The procedures for detecting incidents
- The procedures for investigating incidents
- The procedures for containing incidents
- The procedures for recovering from incidents
By implementing these policies and controls, organizations can improve their ability to identify, assess, and mitigate risks to their assets. This can help to protect organizations from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of their assets.
Here is a table that summarizes the relationship between the ISO 27001 standards and the policies mentioned above:
| Policy | Relevant ISO 27001 Standards |
|---|---|
| Asset Inventory Policy | 5.9.1 Asset inventory, 8.2.1 Information classification, 8.2.2 Information labelling, 8.8.1 Technical vulnerability identification |
| Asset Classification Policy | 8.2.1 Information classification |
| Asset Management Policy | 5.9.1 Asset inventory, 8.1.3 Acceptable use of assets, 8.2.1 Information classification, 8.2.2 Information labelling, 8.8.1 Technical vulnerability identification, 8.8.2 Technical vulnerability remediation |
| Vulnerability Management Policy | 8.8.1 Technical vulnerability identification, 8.8.2 Technical vulnerability remediation |
| Incident Response Policy | 11.4 Incident response |
The following ISO 27001 standards and ISO 27002 ISMS documents are relevant to the policies mentioned above:
-
Asset Inventory Policy: This policy is relevant to the following ISO 27001 standards and ISO 27002 ISMS documents:
- 5.9.1 Asset inventory (ISO 27001)
- 8.2.1 Information classification (ISO 27002)
- 8.2.2 Information labelling (ISO 27002)
- 8.8.1 Technical vulnerability identification (ISO 27002)
-
Asset Classification Policy: This policy is relevant to the following ISO 27001 standards and ISO 27002 ISMS documents:
- 8.2.1 Information classification (ISO 27002)
-
Asset Management Policy: This policy is relevant to the following ISO 27001 standards and ISO 27002 ISMS documents:
- 5.9.1 Asset inventory (ISO 27001)
- 8.1.3 Acceptable use of assets (ISO 27002)
- 8.2.1 Information classification (ISO 27002)
- 8.2.2 Information labelling (ISO 27002)
- 8.8.1 Technical vulnerability identification (ISO 27002)
- 8.8.2 Technical vulnerability remediation (ISO 27002)
-
Vulnerability Management Policy: This policy is relevant to the following ISO 27001 standards and ISO 27002 ISMS documents:
- 8.8.1 Technical vulnerability identification (ISO 27002)
- 8.8.2 Technical vulnerability remediation (ISO 27002)
-
Incident Response Policy: This policy is relevant to the following ISO 27001 standards and ISO 27002 ISMS documents:
- 11.4 Incident response (ISO 27001)
These are just some of the ISO 27001 standards and ISO 27002 ISMS documents that are relevant to the policies mentioned above . There may be other documents that are also relevant, depending on the specific requirements of your organization.
It is important to note that the ISO 27001 standards and ISO 27002 ISMS documents are just a set of guidelines. They do not provide specific requirements that must be met. Organizations are free to implement the controls that are most appropriate for their specific needs.
If you are unsure of which controls you need to implement, you may want to consult with a security professional. They can help you assess your organization’s risk and recommend the appropriate controls.
Here is a table that maps the CIS Controls to ISO 27001, PCI DSS, NIST, and SOC 2:
| CIS Control | ISO 27001 | PCI DSS | NIST | SOC 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Implement a risk management program | 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 | 4, 12, 13 | 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 | 1, 2, 4 |
| 2. Implement a change management process | 4.2, 4.3, 4.4 | 8, 9, 10 | 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 | 3, 5, 6 |
| 3. Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication | 8.2.1, 8.2.2 | 6, 8 | 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 | 7, 8, 9 |
| 4. Segment the network | 10.4 | 11 | 10.1, 10.2, 10.3 | 10, 11, 12 |
| 5. Monitor and analyze logs | 12.1, 12.2 | 10, 11 | 12.1, 12.2 | 13, 14 |
| 6. Use security tools and technologies | 13.1, 13.2, 13.3 | 1, 2, 3 | 13.1, 13.2, 13.3 | 15, 16, 17 |
| 7. Educate and train employees | 14.1, 14.2 | 14 | 14.1, 14.2 | 18, 19 |
| 8. Develop and implement incident response plans | 16.1, 16.2 | 15 | 16.1, 16.2 | 20, 21 |
| 9. Maintain a secure configuration | 17.1, 17.2 | 7 | 17.1, 17.2 | 22, 23 |
| 10. Protect data in transit and at rest | 18.1, 18.2 | 5, 6 | 18.1, 18.2 | 24, 25 |
“Disclaimer: This table is not exhaustive, and there may be other mappings that are not listed here. It is important to consult with a security professional to ensure that your organization is in compliance with all applicable standards and regulations.”
I have also listed here the document numbers in ISO 27001:2022 and 27002:2022 and other ISMS standards that are relevant to each of the 5 CIS Control 1 safeguards:
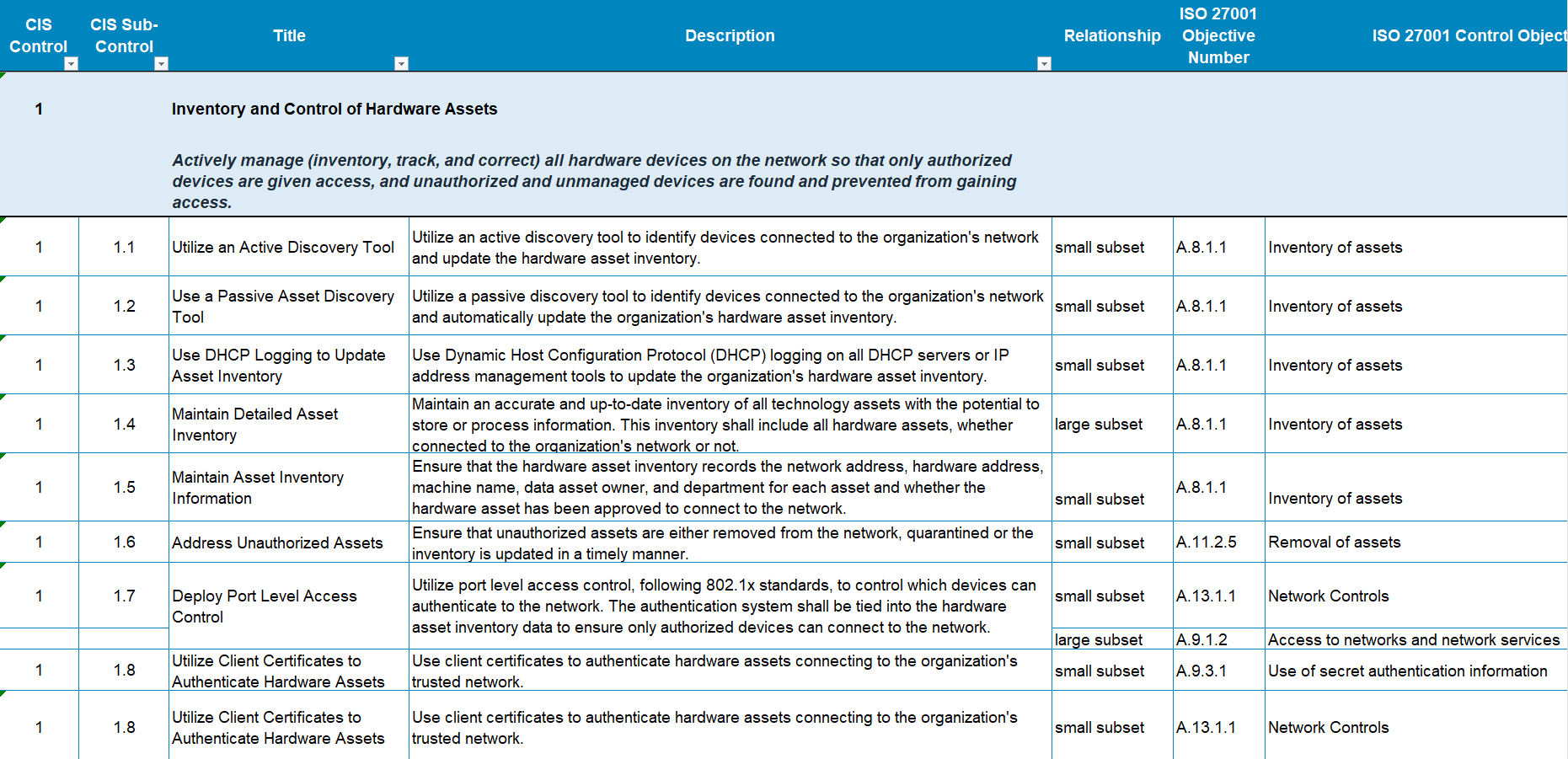
Safeguard 1: Establish and Maintain Detailed Enterprise Asset Inventory
- ISO 27001:2022 – 4.2.1: Information asset inventory
- ISO 27002:2022 – 5.1: Information classification
- ISO 27002:2022 – 5.2: Information ownership
- ISO 27002:2022 – 5.3: Asset management
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 – Information security management systems (ISMS) – 12.2.1
- ISO/IEC 27002:2022 – Code of practice for information security management (ISMS) – 10.1
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) – 12.2
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Security Rule – 164.308(a)(1)(ii)
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) Section 404 – 302(a)(2)(A)(ii)
- Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) – 3.1.1
- SOC 2 – Security
- NIST – Identify
- GDPR – Pseudonymization and encryption of personal data
Safeguard 2: Address Unauthorized Assets
- ISO 27001:2022 – 4.2.2: Access control
- ISO 27002:2022 – 6.3: Access control
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 – ISMS – 12.2.2
- ISO/IEC 27002:2022 – ISMS – 10.2
- PCI DSS – 12.3
- HIPAA Security Rule – 164.308(a)(1)(iii)
- SOX Section 404 – 302(a)(2)(A)(iii)
- FISMA – 3.1.2
- SOC 2 – Availability
- NIST – Protect
- GDPR – Implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of personal data
Safeguard 3: Utilize an Active Discovery Tool
- ISO 27001:2022 – 10.2: Network security
- ISO 27002:2022 – 12.1: Network security
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 – ISMS – 12.2.3
- ISO/IEC 27002:2022 – ISMS – 10.3
- PCI DSS – 12.4
- HIPAA Security Rule – 164.308(a)(1)(iv)
- SOX Section 404 – 302(a)(2)(A)(iv)
- FISMA – 3.1.3
- SOC 2 – Processing Integrity
- NIST – Detect
- GDPR – Taking steps to ensure that only authorized persons have access to personal data
Safeguard 4: Use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Logging to Update Enterprise Asset Inventory
- ISO 27001:2022 – 10.2: Network security
- ISO 27002:2022 – 12.1: Network security
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 – ISMS – 12.2.4
- ISO/IEC 27002:2022 – ISMS – 10.4
- PCI DSS – 12.5
- HIPAA Security Rule – 164.308(a)(1)(v)
- SOX Section 404 – 302(a)(2)(A)(v)
- FISMA – 3.1.4
- SOC 2 – Confidentiality
- NIST – Respond
- GDPR – Responding to requests from individuals for access to their personal data
Safeguard 5: Use a Passive Asset Discovery Tool
- ISO 27001:2022 – 10.2: Network security
- ISO 27002:2022 – 12.1: Network security
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 – ISMS – 12.2.5
- ISO/IEC 27002:2022 – ISMS – 10.5
- PCI DSS – 12.6
- HIPAA Security Rule – 164.308(a)(1)(vi)
- SOX Section 404 – 302(a)(2)(A)(vi)
- FISMA – 3.1.5
- SOC 2 – Privacy
- NIST – Recover
- GDPR – Reporting data breaches to the supervisory authority
Communication Plan
The following communication plan has been developed to keep stakeholders informed of the progress of the project:
- Weekly status meetings will be held with stakeholders.
- A monthly progress report will be sent to stakeholders.
- A final report will be presented to stakeholders at the end of the project.
Approvals
The following approvals are required for this project:
- Project charter
- Project plan
- Final report
Conclusion
This scope of work plan provides a detailed overview of the steps that will be taken to implement the CIS control 1 (Control 01: Inventory and Control of Enterprise Assets) at your organization. By following this plan, we can ensure that organization has a comprehensive understanding of its assets and that its systems and data are protected from unauthorized access.
Search terms related to this article include: Information security controls, Hardware inventory, Hardware control, Software inventory, Software control, Data protection, Data security, Secure configuration, Configuration management, Account management, Password management, Access control, Privilege management, Vulnerability management, Patch management, Audit log management, Security logging, Email protection, Web browser protection, Malware defense, Antivirus, Antimalware, Data recovery, Disaster recovery, Network security, Port security, Protocol security, Network monitoring, Intrusion detection, Intrusion prevention, Application security, Software security, Wireless security, Wifi security, Physical security, Environmental security, Incident response, Security incident management, Business continuity, Disaster recovery, Penetration testing, Cybersecurity, CIS Controls v8, CIS Controls 18, CIS Controls list, CIS Controls framework, Phishing, Vulnerability management, Security awareness training, Phishing and social engineering, Password security, Data protection, Secure computing practices, Incident response.







